Auch die Population der Magellanpinguine unterliegt starken Schwankungen. An der südamerikanischen Küste nimmt der Bestand in einigen Kolonien zu, in anderen ab (1). Die Population auf den Falklandinseln ist in den letzten Jahrzehnten stark abgesunken, wobei auch hier die Ursachen noch unbekannt sind. Der ART hat die allgemeine Brutbiologie der Magellanpinguine auf den Falklands (2) als auch die Bestandsentwicklung und die Nahrung untersucht (3,4). Auch die Nahrungsgebiete während der Brutzeit (5) und in den Wintermonaten (6) konnten mittels Satellitentelemetrie eingegrenzt werden. Vergleichende Untersuchungen zur Ernährungsökologie fanden auf der Isla Martillo im Beagle Kanal, Argentinien (7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15), der Isla de los Estados, Argentinien (16,17,18), und auf den Islotas Punihuil, Chile (19,20,21,22) statt, wo die Magellanpinguine gemeinsam mit Humboldtpinguinen vorkommen. Demach sterben viele Pinguine als Folge von Fischerei (23) und Umweltverschmutzung nicht nur auf den Falklands, sondern auch in den Nahrungsgebieten während und außerhalb der Brutzeit entlang der südamerikanischen Küste (24).
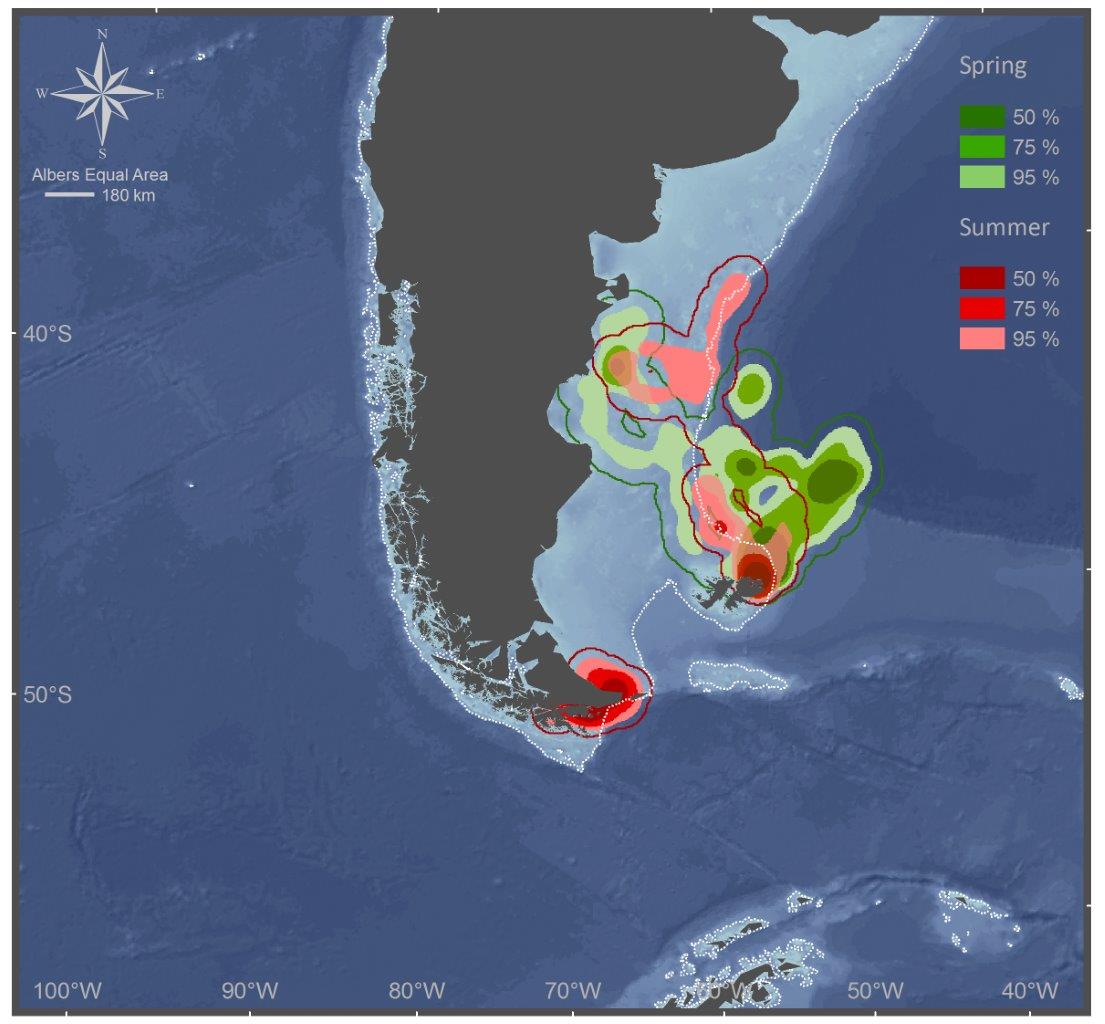
Nahrungsgebiete der Magellanpinguine in Frühling und Sommer

Verteilung von Magellanpinguinen im Winter (grün Falklands, rot Isla de los Estados)

Derzeit untersuchen wir weiterhin in Kooperation mit argentinischen Kollegen vom CONICET – CADIC, Ushuaia, die Ernährungsökologie von Magellanpinguinen auf der Isla Martillo und der Isla de los Estados, Argentinien, und Hummock Island, Falklandinseln, in-situ mit Hilfe neu entwickelter Kameralogger.
- (1) Boersma, P.D., E. Frere, O. Kane, L. Pozzi, K. Pütz, A. Raya Rey, G.A. Rebstock, A. Simeone, J. Smith, A. van Buren, P Yorio & P. Garcia Borboroglu (2013) Magellanic Penguin. Pp 233-263 in: García Borboroglu, P.G. & P.D. Boersma (eds.) Penguins – Natural History and Conservation. University of Washington Press, Seattle U.S.A. ISBN 978-0-295-99284-6
- (2) Otley, H.M., A.P. Clausen, D.J. Christie & K. Pütz (2004) Some aspects of the breeding biology of Magellanic penguins in the Falkland Islands. Waterbirds 27: 396-405
- (3) Pütz, K., R.J. Ingham, J.G. Smith & J.P. Croxall (2001) Population trends, breeding success and diet composition of gentoo Pygoscelis papua, magellanic Spheniscus magellanicus and rockhopper Eudyptes chrysocome penguins in the Falkland Islands. Polar Biology 24: 793-807
- (4) Clausen, A.P. & K. Pütz (2002) Recent trends in diet composition and productivity of Gentoo, Magellanic and Rockhopper Penguins in the Falkland Islands. Aquatic Conservation 12: 51-61
- (5) Pütz, K., R.J. Ingham & J.G. Smith (2002) Foraging movements of Magellanic Penguins Spheniscus magellanicus during the breeding season in the Falkland Islands. Aquatic Conservation 12: 75-87
- (6) Pütz, K., R.J. Ingham & J.G. Smith (2000) Satellite tracking of the winter migration of Magellanic Penguins Spheniscus magellanicus breeding in the Falkland Islands. Ibis 142: 614-622
- (7) Raya Rey, A., C.A. Bost, A.C. Schiavini & K. Pütz (2010) Foraging movements of Magellanic penguins in the Beagle Channel, Argentina, related to tide and tidal currents. Journal of Ornithology 151: 933-943
- (8) Pütz, K., A. Schiavini, A. Raya Rey & B.H. Lüthi (2007) Winter migration of magellanic penguins (Spheniscus magellanicus) from the southernmost distributional range. Marine Biology 152: 1227-1235
- (9) Raya Rey, A., K. Pütz, G. Scioscia, B. Lüthi & A. Schiavini & (2012) Sexual differences in the foraging behaviour of Magellanic Penguins related to stage of breeding. EMU 112(2): 90-96
- (10) Dodino, S., L. Riccialdelli, M.J. Polito, K. Pütz & A. Raya Rey (2020) Inter-annual variation in the trophic niche of Magellanic penguins Spheniscus magellanicus during the pre moult period at Martillo Island, Tierra del Fuego, Argentina. Marine Ecology Progress Series 655: 215-225
- (11) Harris, S., G. Scioscia, K. Pütz, T. Mattern & A. Raya Rey (2020) Niche partitioning between coexisting Gentoo Pygoscelis papua and Magellanic penguins Spheniscus magellanicus at Martillo Island, Argentina. Marine Biology 167: 105
- (12) Dodino, S., N. Lois, L. Riccialdelli, M. Polito, K. Pütz & A. Raya Rey (2021) Sex-specific spatial use of the winter foraging areas by Magellanic penguins and assessment of potential conflicts with fisheries during winter dispersal. PLoS ONE 16(8): e0256339.
- (13) Harris, S., K. Pütz, T. Mattern, G. Scioscia & A. Raya Rey (2023) The role of conspecifics during pelagic foraging of Magellanic and benthic foraging of Gentoo penguins in the Beagle Channel, Argentina. Marine Biology 170: 17
- (14) Dodino, S., L. Riccialdelli, M.J. Polito, K. Pütz & A. Raya Rey (2023) Variation in the trophic niche and food provisioning between the early and late chick-rearing stages in Magellanic penguins Spheniscus magellanicus at Martillo Island, Tierra del Fuego, Argentina. Marine Biology 170: 96.
- (15) Scioscia, G., S. Harris, A. Schiavini, K. Pütz & A. Raya Rey (2024) Do penguins care about their neighbourhood? Population implications of bioerosion in Magellanic Penguin, Spheniscus magellanicus, at Martillo Island, Beagle Channel, Argentina. PloS ONE 19(11): e03110052
- (16) Rosciano, N., K. Pütz, M.J. Polito & A. Raya Rey (2018) Foraging behaviour of Magellanic Penguins during the early chick rearing period at Isla de los Estados, Argentina. Ibis 160: 327-341
- (17) Dodino, S., L. Riccialdelli, M. Polito, K. Pütz, A. Raya Rey (2022) Intraspecific trophic variation during the early chick-rearing period in Magellanic penguins Spheniscus magellanicus: influence of age and colony. Marine Biology 169: 116
- (18) Dodino, S., L. Riccialdelli, M.J. Polito, K. Pütz, R.L. Brasso & A. Raya Rey (2022) Mercury exposure driven by geographic and trophic factors in Magellanic Penguins from Tierra del Fuego. Marine Pollution Bulletin 174: 113184
- (19) Hiriart-Bertrand, L., A. Simeone, R. Reyes-Arriagada, V. Riquelme, K. Pütz & B. Lüthi (2010) Description of a mixed-species colony of Humboldt (Spheniscus humboldti) and Magallanic Penguins (S. magellanicus) at Metalqui Island, Chiloé, southern Chile. Boletín Chileno de Ornitologia 16(1): 42-47
- (20) Simeone, A., L. Hiriart-Betrand, R. Reyes-Arriagada, M. Halpern, J. Dubach, R. Wallace, K. Pütz & B. Lüthi (2009) Heterospecific pairing and hybridization between wild Humboldt and Magellanic Penguins in southern Chile. Condor 111(3): 544-550
- (21) Raya Rey, A., K. Pütz, L. Hiriart-Bertrand, R. Reyes-Arriagada, V. Riquelme, B. Lüthi & A. Simeone (2013) Comparative foraging behaviour of sympatric breeding Humboldt and Magellanic penguins reveals sex- and species-specific strategies. EMU 113(2): 145-153
- (22) Pütz, K., A. Raya Rey, L. Hiriart-Bertrand, A. Simeone, R. Reyes-Arriagada & B. Lüthi (2016) Post-moult movements of sympatrically breeding Humboldt and Magellanic Penguins in south-central Chile. Global Ecology and Conservation 7: 49-58
- (23) Pütz, K., L. Hiriart-Bertrand, A. Simeone, V. Riquelme, R. Reyes-Arriagada & B. Lüthi (2011) Entanglement and drowning of a Magellanic Penguin (Spheniscus magellanicus) in a gill net recorded by a time-depth recorder in southern Chile. Waterbirds 34(1): 121-125
- (24) Trathan, P.N., P. García-Borboroglu, P.D. Boersma, C.A. Bost, R.J.M. Crawford, G.T. Crossin, R.J. Cuthbert, P. Dann, L.S. Davis, S. de la Puente, U. Ellenberg, H.J. Lynch, T. Mattern, K. Pütz, P.J. Seddon, W. Trivelpiece & B. Wienecke (2014) Pollution, habitat loss, fishing and climate change as critical threats to penguins. Conservation Biology 29(1): 31-41

